INFORMATION REQUEST FORM
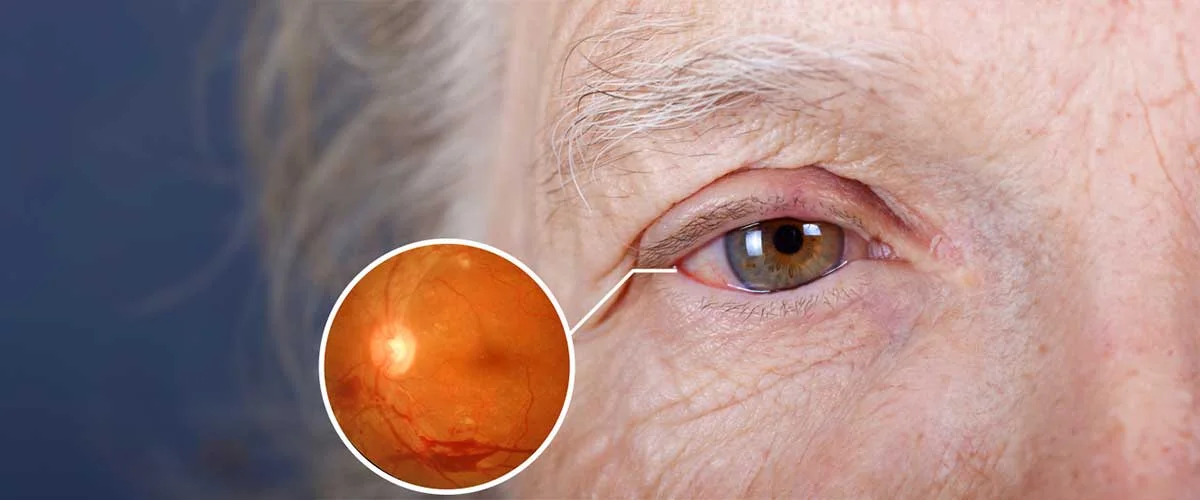
Diabetes (Diabetic Retinopathy)
In addition to causing damage to many organs in our body, diabetes also affects the retina of our eyes, causing Diabetic Retinopathy. The severity of the damage varies depending on the blood sugar level and the duration of the disease.
What are the Diabetic Retinopathy Symptoms?
Diabetes disease affects all the small vessels in our body and affects the retina, which is the layer of the eye rich in nerves and vessels. The earliest findings in diabetic retinopathy are ballooning of small retinal vessels and bleeding in the retinal layers. After these bleedings, blood leaks out of the vessel and edema occurs in the macula, which is the visual center of our eye. As a result, there is a decrease in visual quality and acuity. In advanced cases of diabetic retinopathy, sudden vision loss may occur due to bleeding within the eye. There is usually no complaint of pain in diabetic retinopathy, but in advanced cases, since it is accompanied by increased intraocular pressure, patients may also present with severe pain, depending on the type of glaucoma called Neovascular Glaucoma.
What Tests Are Used to Diagnose Diabetic Retinopathy?
Since Diabetic Retinopathy is a disease that directly affects the retina layer of the eye, the back of the eye (Retina) must be evaluated using drops that dilate the pupils after a detailed vision examination. While edema in the macular region is evaluated with Optical Coherence Tomography, it is also possible to evaluate damaged and leaking retinal vessels with the FFA-Fundus Fluorescein Aniography test.
Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
In Diabetic Retinopathy, it is useful to organize personalized treatment and observe patients closely. It will be necessary to look at the disease not only in terms of eye diseases, but also get help from internal branches such as Endocrine, Nephrology and Cardiology. Treatment of diabetic retinopathy depends entirely on the severity of the disease. While we follow the patient only by observing in early-stage Diabetic Retinopathies, we can benefit from treatment options such as intraocular injections, Laser Treatments or Vitrectomy surgery in more advanced-stage Diabetic Retinopathies.
Laser Photocoagulation Treatment
Laser photocoagulation, which was seen as the first treatment option in diabetic retinopathy in previous years, has now been replaced by intraocular injections. The basic logic of laser photocoagulation treatment, which still has a very important place in the treatment of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy today, is to prevent the formation of unwanted vessels in those areas by burning the non-bleeding areas with laser. In Laser treatment, which is applied in 3-4 sessions with drop anesthesia, patients do not need to be hospitalized after the procedure.
Intraocular Needle Treatment
A wide variety of drugs have been developed for intraocular injection treatments, especially in the last 15 years. The common purpose of these drugs is to prevent unwanted vessels that may form in the eye and to regulate the blood supply of the retina layer of the eye. Intraocular injection treatments are procedures performed under local anesthesia in operating room conditions. Since diabetic retinopathy is a dynamic disease, intraocular needle treatments must be administered by experienced doctors under close monitoring.
Vitrectomy (Retina) Surgery
Another treatment option in cases of diabetic retinopathy that cannot be controlled with injection or laser treatments is vitrectomy surgery. With this surgery, bleeding, membranes or membranes occurring inside the eye can be cleaned. Even if retinal detachment has developed, it can be repaired with surgery. Vitrectomy surgery is a procedure performed under general anesthesia or with sedation anesthesia. After this surgery, which takes approximately 1 hour, patients can be observed in the hospital and discharged on the same day.
The important thing in Diabetic Retinopathy Disease is to detect the disease early. For this, it is recommended to have routine checks for eye diseases once a year and to get support especially from the Endocrine department for diabetes.
You can contact our clinic to get more information about Diabetes (Diabetic Retinopathy) and to make an appointment.
INFORMATION REQUEST FORM
